paper-reading-group
Lottery Ticket Hypothesis
Neural Network pruning. But currently sparse networks cannot be trained from scratch.
Question: Why arent pruned networks trained from scratch?
The Hypothesis
Lottery Ticket Hypothesis: Dense, randomly-initialized, feed-forward networks contain subnetworks (winning tickets) that when trained in isolation reach test accuracy comparable to the original network in a similar number of iterations.
Algorithm 1: Pruning
-
Randomly initialize a neural network: $f(x; \theta_{0}) \ where \ \theta_{0} \text{\textasciitilde} D_{\theta}$
- Train the network for $j$ iterations
- Prune $p \%$ of the network (through some algorithm).
- Reset the remaining weights to values in $\theta_{0}$, and hence the winning ticket $f(x;\ m \bigodot \theta_{0})$ .
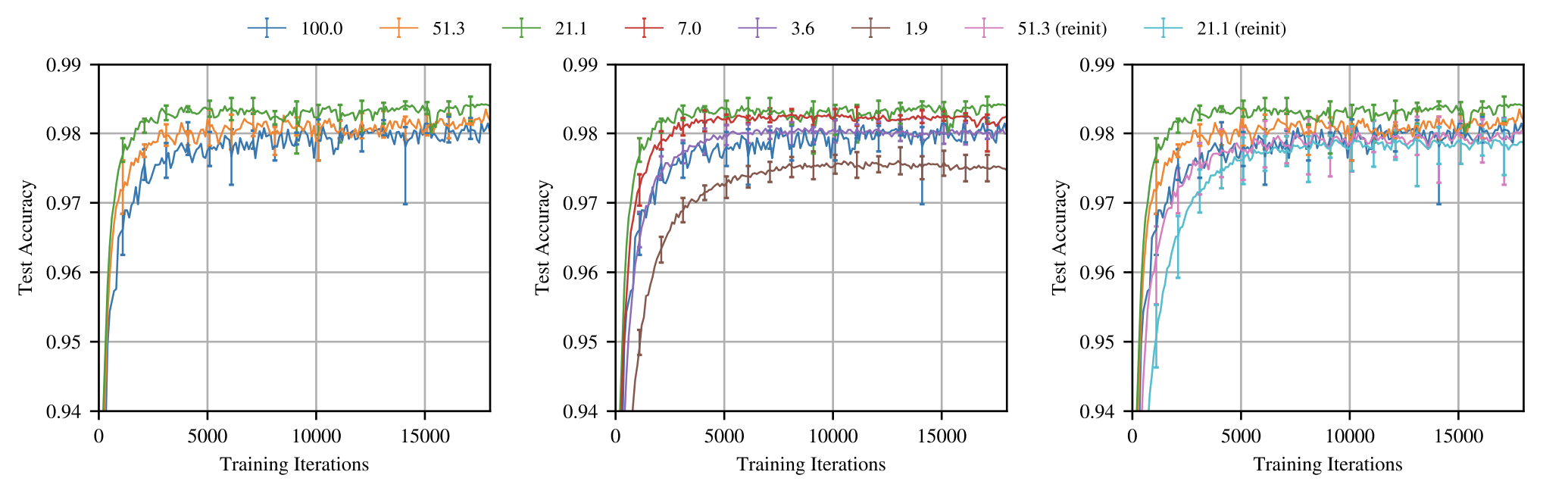
Figure 1: The legends represent Sparsity mask = 1 - Percentage of weights pruned. So 100% sparsity mask correspondings to 0% weights pruned. Pruned network performance with sparsity mask 21% is highest.
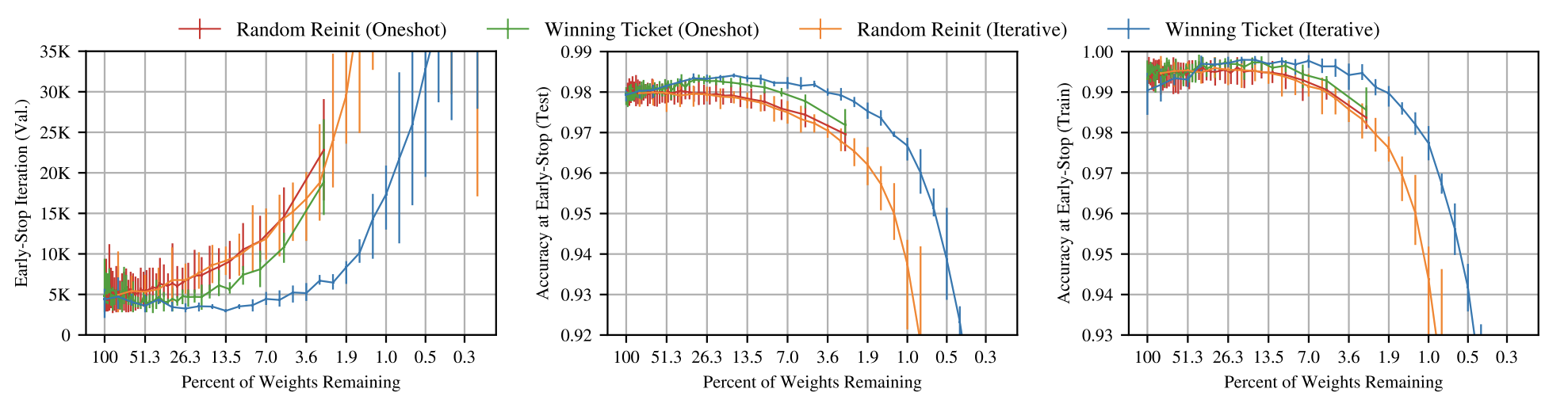
Figure 2: Early stop iteration increases with higher sparsity.
Algorithm 2: Iterative Pruning
- Perform a step of finding the lottery ticket and prune by 20%
- Repeat
Algorithm 3: One Shot Pruning
- Is essentially Algorithm 1.
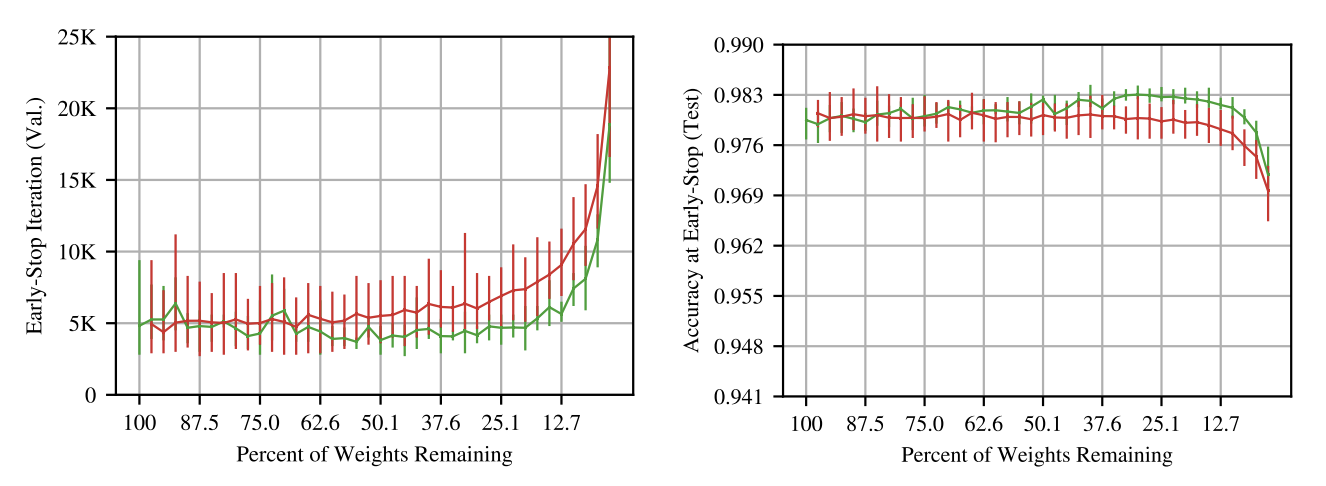
Figure 3: One shot pruned tickets are also winning tickets.
Convolutional Neural Networks
Whats the difference?
- Shared weights. Hence computation is very sensitive.
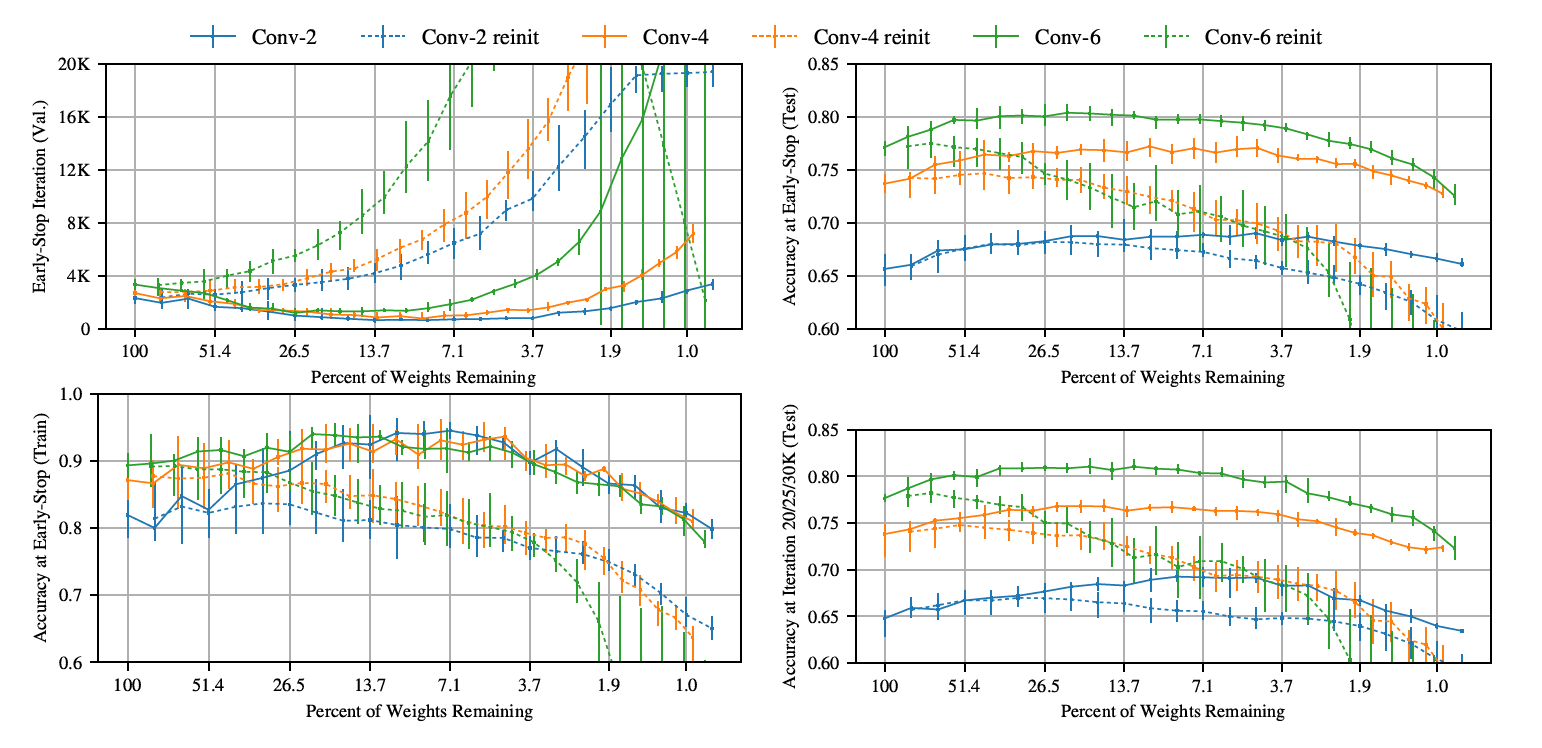
Figure 4: CNNs also have winning tickets!
Dropout
Whats the difference?
- Connections are randomly removed during training.
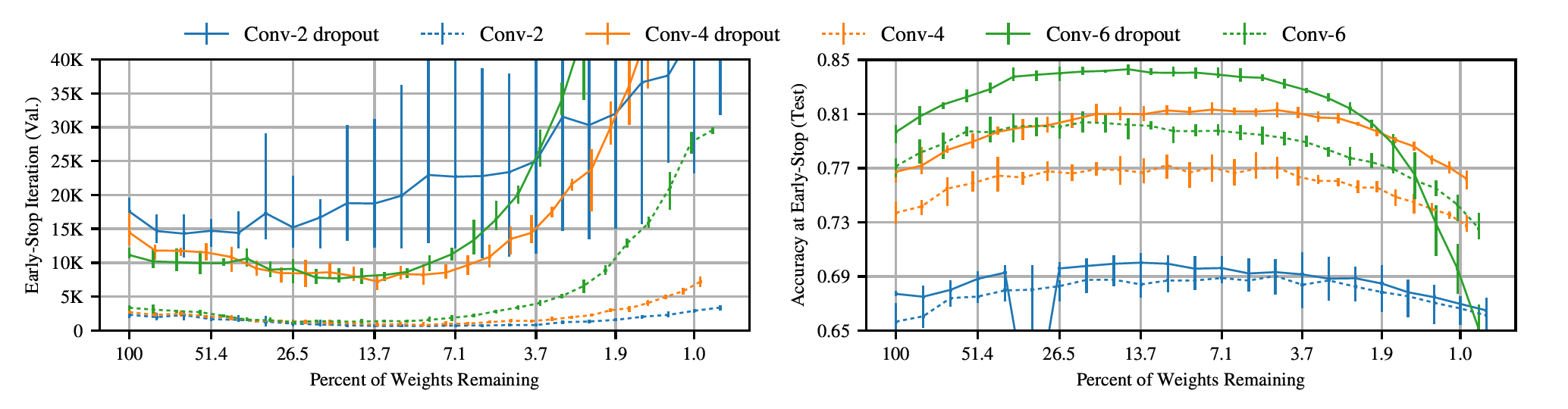
- Better winning tickets than even usual ones. (Rigging the lottery).
Discussion
- Do these tickets come from having the same initial distribution as the final one? No. Check Appendix F.
- Reinitializing to the same distribution is almost the same as having an inductive bias.
- Winning tickets exceed performance of original tickets? A very known result even in the literature surrounding Quantized networks perform better than original overparameterised networks.
-
Deeper networks require learning rate warmup.
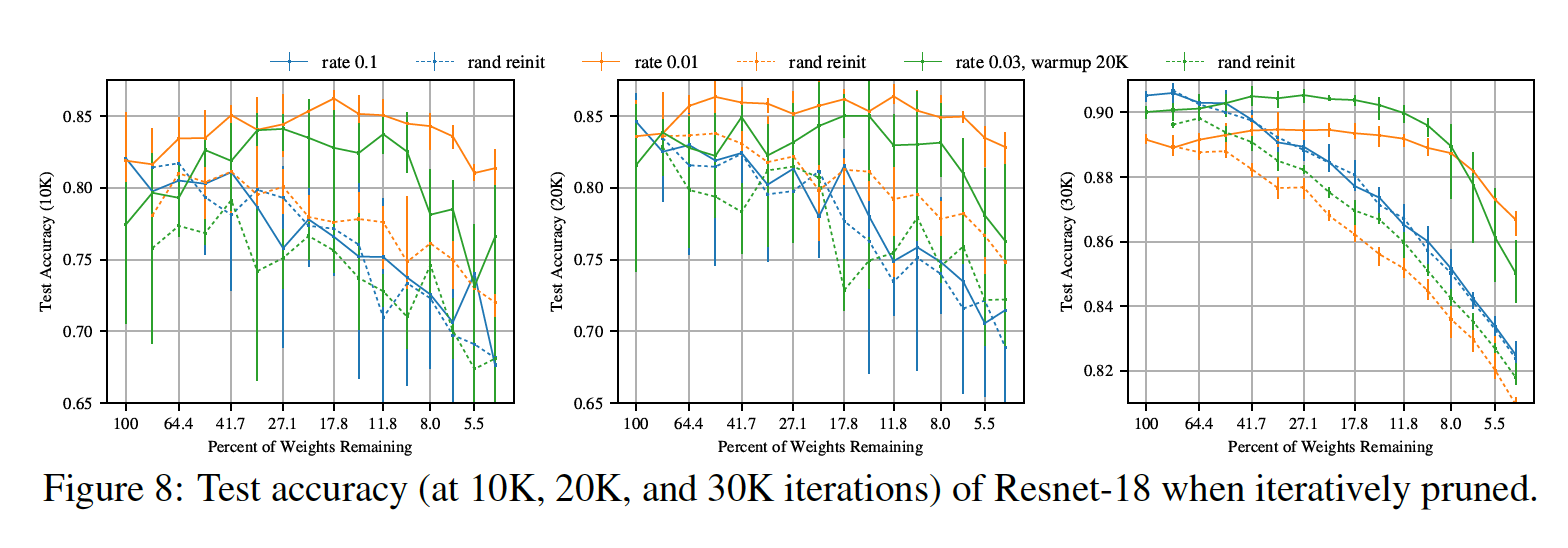
Future work
- Structured pruning
- Non-magnitude based pruning
- Extension to Language Models